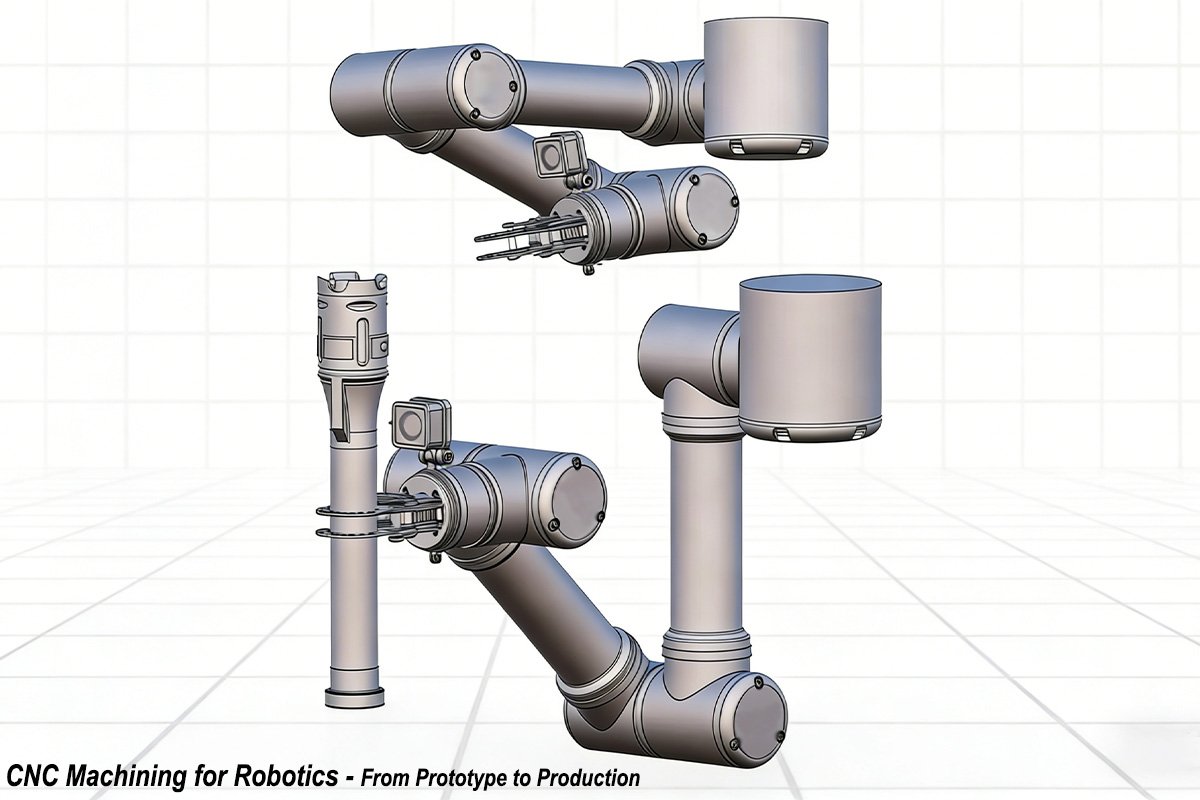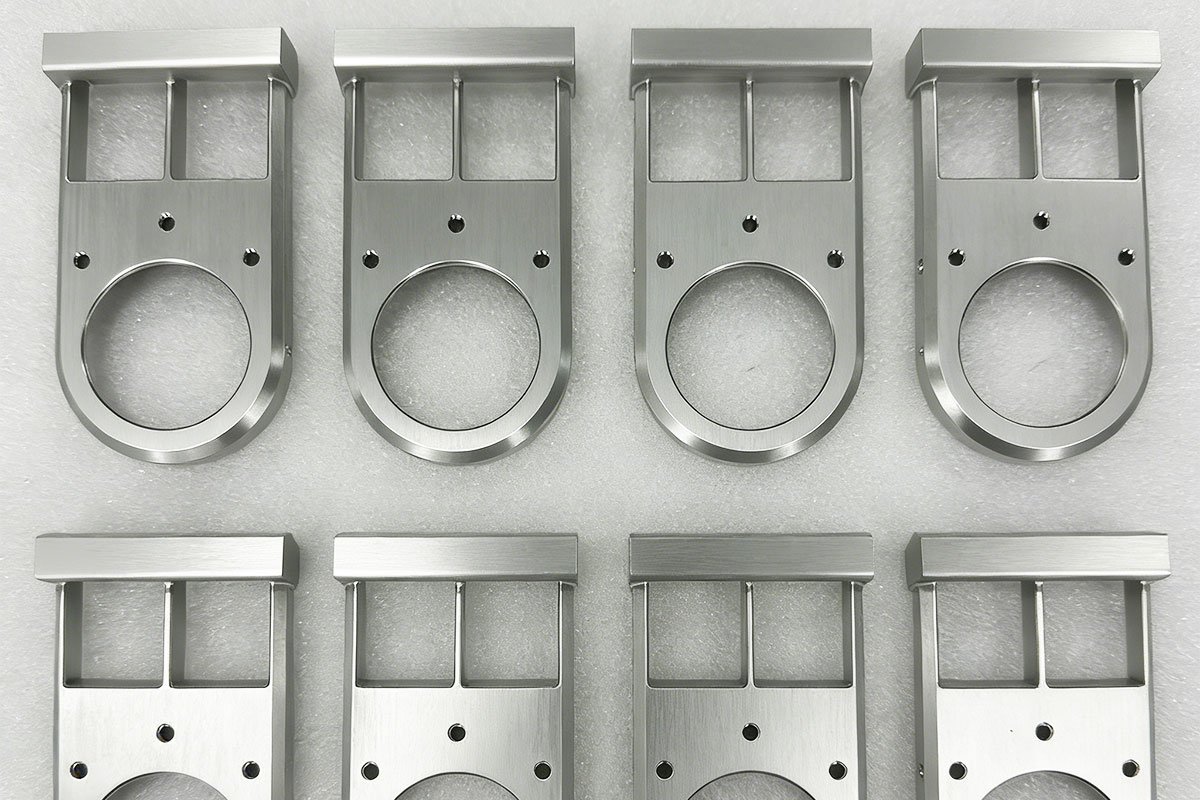
Why CNC Machining is Critical for Custom Automation Parts Manufacturing
We’ve all been there—you have a perfect design for a new machine, but the standard off-the-shelf parts just don’t fit. They are either the wrong size, too heavy, or just not tough enough for the job.
You shouldn’t have to change your design just because a standard part doesn’t exist. That’s why custom automation parts manufacturing is a game-changer. It gives you the freedom to create exactly what you need, not just what’s available in a warehouse. Whether it’s a weirdly shaped bracket or a specialized robotic gripper, CNC machining allows you to turn those complex ideas into real, working automatic machine parts quickly.
Why Go Custom? The Real Value of Bespoke Automation Parts
Standard parts are great for nuts, bolts, and bearings. They are cheap and you can get them tomorrow. But when it comes to the core components of your machine—like the grippers, brackets, or specialized housings—relying on a catalog often leads to compromises.
Here is why switching to custom automation parts manufacturing is often the smarter choice for your production line:
Stop Designing “Around” the Catalog
When you use standard parts, you are forced to design your machine based on what is available in a book. It limits your creativity.With custom CNC machining, you have total design freedom. You can design the part exactly how it needs to be to fit into tight spaces or handle complex movements. You don’t have to waste time figuring out adapters or shims to make a standard part fit. You just make the part that fits perfectly.
Get the Right Material for the Job
Catalog parts usually come in generic materials—mostly standard steel or aluminum. But automation often needs something specific.
- Need a robot arm to move faster? You need lightweight aluminum (7075) to reduce inertia.
- Handling food products? You need Stainless Steel 316 that won’t rust.
- Need a low-friction guide? You might need Delrin (POM) or PEEK.
Using custom manufacturing, you pick the exact material that ensures your automation system lasts longer and runs smoother.
Simpler Assembly, Fewer Failures
A standard solution might require you to bolt three different parts together to do one job. That’s three times the weight and three places where screws can vibrate loose.
A custom machined part can combine all those features into a single, solid piece. Fewer parts mean less assembly time and fewer things that can go wrong when the machine is running 24/7.
Keeping Old Machines Alive (Spare Parts)
This is a huge one. Sometimes, you have a perfectly good machine, but the original manufacturer went out of business, or they stopped making the spare parts.
You don’t need to scrap the whole machine. We can take the broken part, reverse-engineer it, and use CNC machining to create a brand-new replacement that is often better than the original. It’s the fastest way to solve the “obsolete part” headache.
How We Build Them: Manufacturing Processes That Matter
You have your CAD files ready, but how do we turn those digital designs into metal or plastic parts? In the world of custom automation parts manufacturing, there is no “one size fits all” method.
Here are the main techniques we use to build parts that fit your machine perfectly:
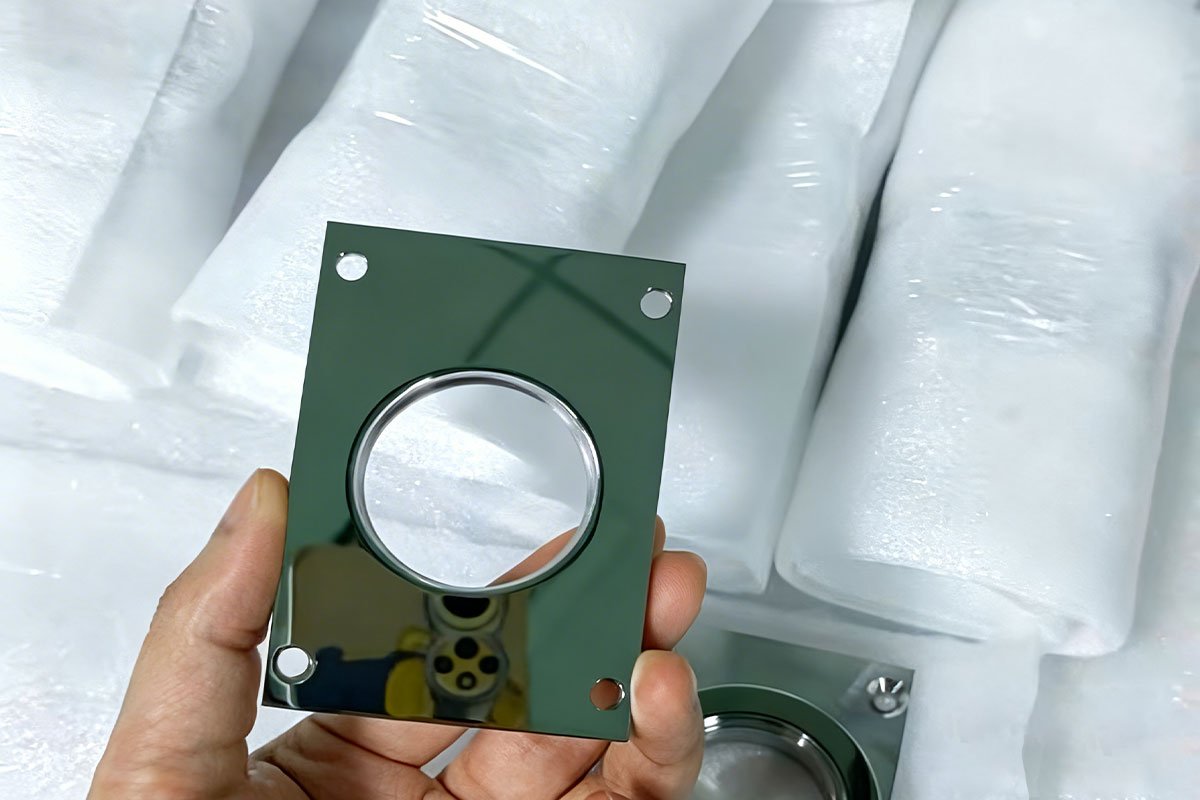
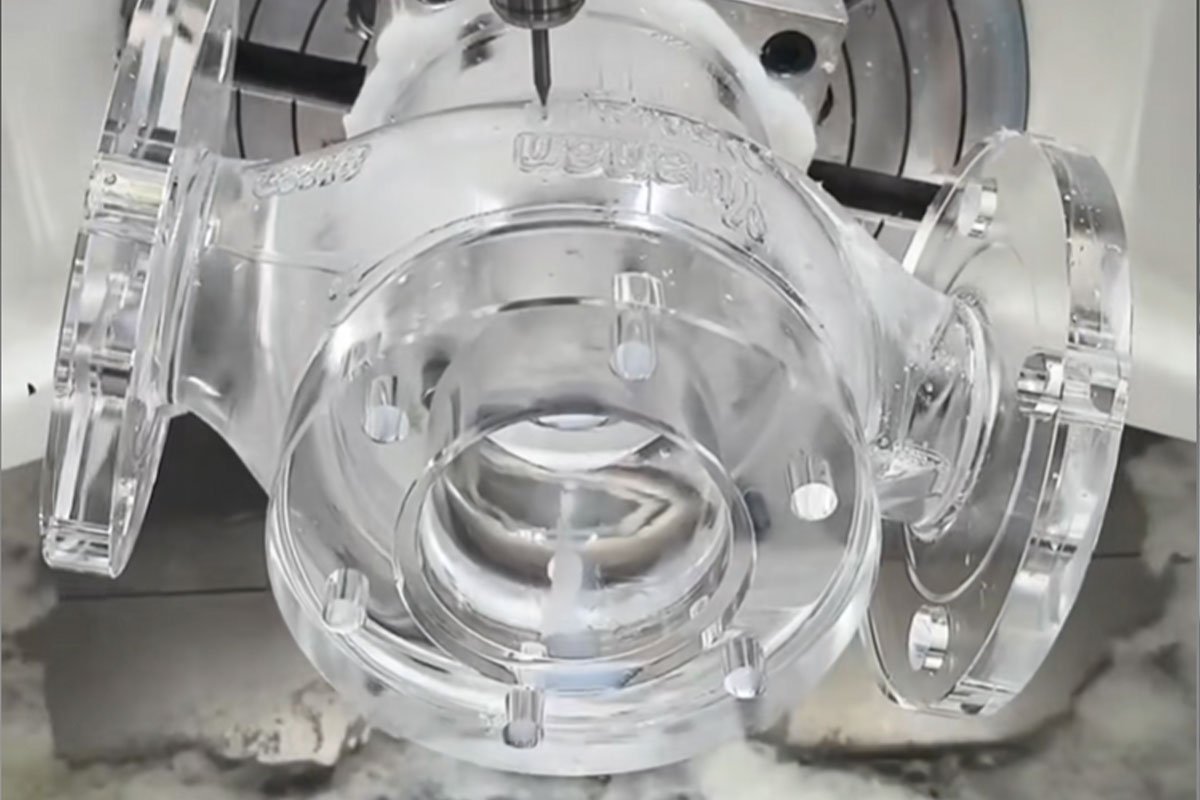
CNC Milling (For the Boxy & Complex Stuff)
Think of this as the bread and butter of automation manufacturing. If your part isn’t round (like a bracket, a housing, or a mounting plate), we probably use CNC Milling.
What it makes: Custom base plates, robotic arm links, and sensor housings.
Why use it: It’s incredibly versatile. We use high-speed cutters to carve material out of a solid block. For those really tricky shapes with curves and angles—like a complex robot joint—we use 5-Axis CNC Machining. It lets us machine the part from all sides in one go, which means better accuracy and faster delivery for you.
CNC Turning (For the Round & Spinny Stuff)
If your part is cylindrical, CNC Turning (or Lathe work) is the way to go. The material spins at high speed while a tool shaves it down.
What it makes: Drive shafts, rollers, leadscrew nuts, and custom pins.
Why use it: It’s the best way to get perfect concentricity (making sure the center is actually the center). If your automation system has high-speed moving parts, like a conveyor roller, you need the precision that turning provides to avoid vibration.
EDM (Wire & Sinker)
Sometimes, a drill bit just can’t reach a tight corner, or the material is too hard to cut. That’s where EDM comes in. It uses electricity to cut through metal. We use this for internal keyways or sharp corners in custom grippers and fixtures where a rotating tool simply won’t fit.
Surface Finishing (The “Make It Last” Step)
A fresh-off-the-machine part is great, but in automation, it usually needs a shield. Raw metal can corrode, conduct electricity when you don’t want it to, or wear out too fast.
Anodizing: The standard for aluminum automation parts. It makes the surface harder and scratch-resistant. Plus, you can color-code parts (like blue for air lines, red for sensors) to make assembly easier.
Electroless Nickel Plating: Perfect for steel parts in packaging machines. It’s smooth, hard, and protects against rust without changing the part’s dimensions too much.
Bead Blasting: Gives parts that nice, matte, professional look that hides tool marks.
Picking the Right Stuff: Materials for Automation
In automation, material selection is everything. If a part is too heavy, your motor has to work harder. If it’s too soft, it wears out in a week. We work with dozens of materials, but for custom automation parts, these four categories cover about 90% of what our clients need.
Aluminum
In robotics and high-speed pick-and-place systems, you want Low Inertia. Aluminum is lightweight but strong. Use 7075 Aluminum if you need the strength of steel but the weight of aluminum.
Common Grades: 6061-T6, 7075-T6
Best for:
Robot Arms & End Effectors: Moving fast without burning out servo motors.
Gantry Plates: Structural parts that need to slide back and forth quickly.
Sensor Brackets: Easy to machine and cheap.
Stainless Steel
No one likes a rusty machine, especially if you are making food or medicine. Stainless steel handles daily washdowns and harsh chemicals without complaining.
Common Grades: 304, 316L, 17-4PH
Best for:
Food Packaging Parts: Guide rails, filling nozzles, and hoppers.
Medical Device Assembly: Parts that need to be sterilized.
Outdoor Automation: Equipment exposed to rain or salt air.
Carbon & Alloy Steel
When aluminum is too soft and stainless is too expensive, plain old steel is the answer. It’s tough, hard, and magnetic.
Common Grades: 1045, 4140, A2/D2 Tool Steel
Best for:
Drive Shafts & Axles: Parts that transmit high torque.
Base Plates: Heavy stationary parts where weight helps dampen vibration.
Wear Parts: For grippers that touch abrasive materials, we use hardened Tool Steel (A2/D2) so they don’t wear down.
Engineering Plastics
Metal-on-metal friction is loud and messy (requires grease). Plastics are often self-lubricating, quiet, and gentle on the products being handled.
Common Grades: Delrin (Acetal/POM), PEEK, UHMW, Nylon
Best for:
Bushings & Bearings: Sliding parts that need low friction.
Star Wheels & Guides: In bottling lines, plastics won’t scratch the glass bottles or crush the cans.
Wear Strips: Underneath conveyor chains to reduce noise.
Case Study: High-Speed Automatic Carton Erector
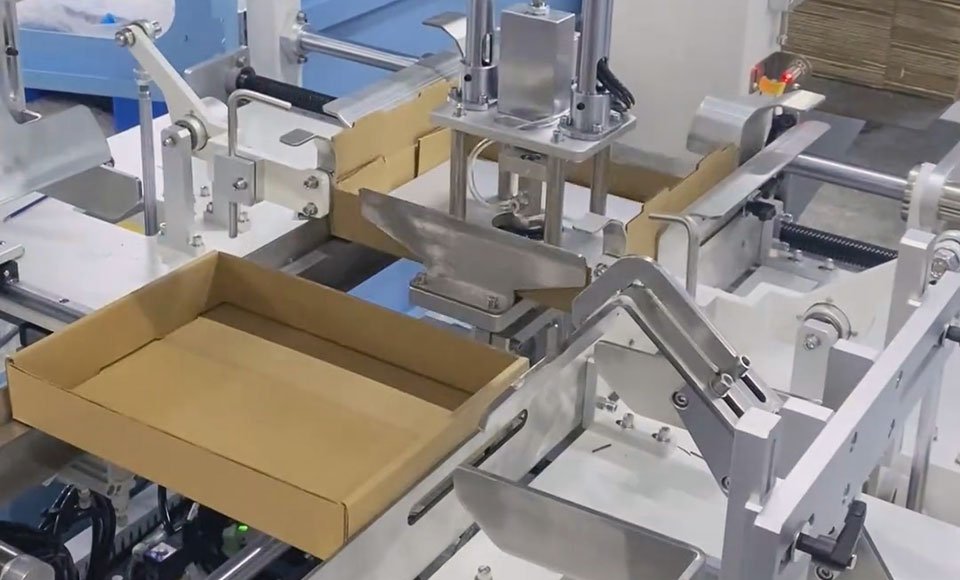

How Precision CNC Components Solved the E-commerce Bottleneck
In the fast-paced world of e-commerce fulfillment, manual carton folding is a costly bottleneck. To solve this problem, the customer designed a high-speed automatic carton erector that can form 50 cartons per minute, which adopts our CNC machining services.
However, a machine is only as reliable as its parts. Here is how our custom CNC machining services ensured the performance of the four critical subsystems:
The Feeding Unit: Preventing Jams at the Source
The Part: Custom Transmission Shafts & Positioning Pins.
The board feeder holds up to 1,000 flat corrugated boards. To ensure they feed one by one without double-feeding or jamming, we machined the transmission components with tight concentricity. Stable, continuous feeding even during 24/7 high-volume shifts.
The Folding Mechanism: Withstanding Mechanical Stress
The Part: Heavy-Duty Linkage Arms & Pressing Blocks.
These components are CNC-milled from solid alloy steel blocks, ensuring structural integrity and precise geometry for the bottom flap folding motion.
The Positioning System: Guaranteeing Squareness
The Part: Precision Side Clamp Jaws & Adjustment Brackets.
A carton must be perfectly square, or it won’t fit the packer later. We machined the side clamps to a ±0.05mm tolerance.
The Pneumatic Control: Speed Through Air Flow
The Part: Custom Aluminum Manifolds & Valve Blocks.
To eliminate air leakage issues, the customer replaced generic leak-prone connectors with CNC-machined custom valve blocks, engineered with ultra-smooth internal passages and precision interface finishes. The result? Drastically reduced air loss, faster cylinder actuation, and a tangible leap in the machine’s high-speed production capacity.
Whether you need a complex pneumatic block or a high-wear linkage, we deliver CNC parts that make your automation system reliable.
Share this article
Written by : Alex
A quick overview of the topics covered in this article.
Latest articles
March 3, 2026