Understanding Aluminum CNC Prototype Machining
Prototyping is a critical phase in product development, enabling engineers and designers to evaluate a design’s form, fit, and functionality. When using traditional machining methods, creating aluminum prototypes can be costly and time-intensive. However, Aluminum CNC prototype machining offers a faster, more cost-effective solution. By leveraging advanced CNC technology, it’s now possible to produce high-precision aluminum prototypes quickly, with excellent surface finishes and tight tolerances—ideal for functional testing, design validation, and small-batch production.
What is Prototype Machining?
Prototype machining is a manufacturing process used to produce early versions of a product, typically using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines. It involves creating a small number of parts—often just one or a few—to evaluate the design’s appearance, fit, and function.
The main goal is to turn a digital 3D model into a physical part, so engineers and designers can see how the final product will look and perform. This helps identify potential issues such as design flaws, assembly problems, or material limitations early in the development process.
By detecting and correcting these issues before mass production begins, companies can avoid costly mistakes and reduce time-to-market. CNC prototype machining is especially valuable because it offers high precision, fast turnaround times, and the ability to work with real engineering materials like aluminum, steel, and plastics.
In short, prototype machining bridges the gap between concept and production, making product development more efficient and reliable.
Why Choose Aluminum for Your Prototype?
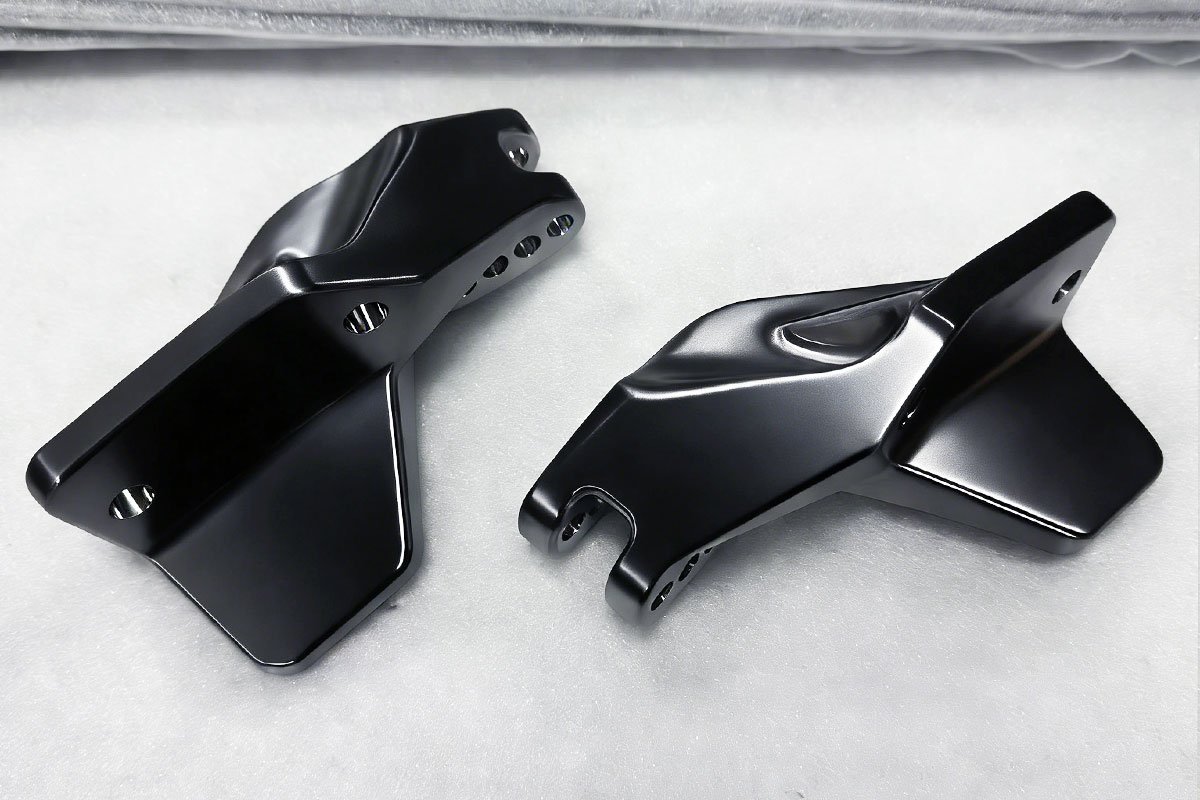
When developing a new product, choosing the right material for your prototype is important. Aluminum is one of the most popular choices for prototyping, especially in CNC prototype machining. It offers a strong combination of performance, cost, and ease of manufacturing.
1. Lightweight and Durable
Aluminum has a high strength-to-weight ratio. This makes it ideal for prototypes used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics, where reducing weight without sacrificing strength is essential.
2. Easy to Machine
Aluminum is highly machinable, meaning it can be cut, drilled, and shaped quickly and accurately with CNC machines. This helps reduce production time and cost, especially for complex designs. The result is a high-quality aluminum CNC prototype with smooth surfaces and tight tolerances.
3. Cost-Effective
Compared to other metals like stainless steel or titanium, aluminum is more affordable. This helps keep prototype costs low, which is especially important when testing multiple design iterations.
Common Aluminum Alloys for Prototyping
When creating an aluminum prototype using CNC prototype machining, selecting the right alloy is essential. Different aluminum alloys offer varying levels of strength, machinability, corrosion resistance, and weight—factors that directly impact how well your prototype performs during testing.
Below are the most commonly used aluminum alloys in prototyping:
- 6061-T6 – The Most Popular Choice
Aluminum 6061-T6 is the most widely used alloy for prototypes. It offers a balanced mix of good mechanical properties, excellent corrosion resistance, and high weldability. It is easy to machine, making it ideal for complex parts with tight tolerances.
Best for: General-purpose prototypes, consumer products, enclosures, brackets, and automotive parts.
- 7075-T6 – High Strength for Demanding Applications
It has a very high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for applications where performance is critical. While slightly more expensive and less corrosion-resistant than 6061, it is often chosen when maximum strength is required.
Best for: Aerospace components, drone parts, high-stress mechanical parts, and defense applications.
Choosing the Right Alloy
The best alloy for your aluminum CNC prototype depends on your design requirements—such as strength, weight, environment, and manufacturing process. Most prototyping projects start with 6061-T6 due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Need help? You can contact our mechanical engineers to discuss your project – it’s completely free. We’ll help you choose the right aluminum alloy for your project and provide fast, precise CNC prototype machining services.
How CNC Machining Speeds Up Prototype Development
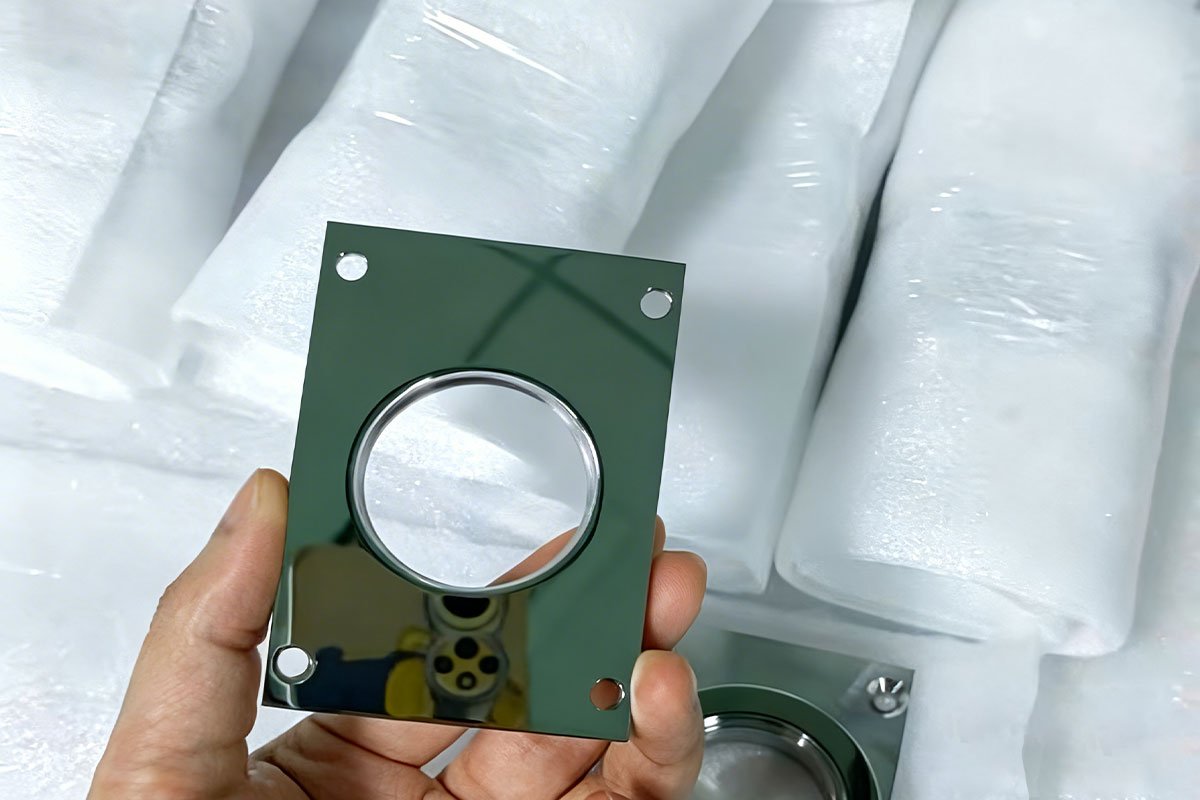
CNC machining is a precise, fast, and versatile prototyping method. It uses computer-controlled machines to cut materials like aluminum, steel, and engineering plastics based on a 3D CAD model, achieving tight tolerances—typically ±0.01 mm—ensuring the prototype accurately reflects the final product.
Unlike injection molding, which requires costly molds and long lead times, CNC machining starts quickly after design approval. Once the CAD file is converted to G-code via CAM software, production begins immediately, supporting faster design iterations and shorter development cycles.
Compared to 3D printing—commonly used for visual models with layered plastics—CNC machining removes material from a solid block, producing stronger, more durable parts with better mechanical properties. This makes it ideal for functional testing under real-world conditions.
For consumer products, industrial components, or electronic enclosures, CNC prototype machining offers a reliable and cost-effective way to validate designs before mass production.
Common CNC Machining Operations Used in Prototyping
CNC MIlling:
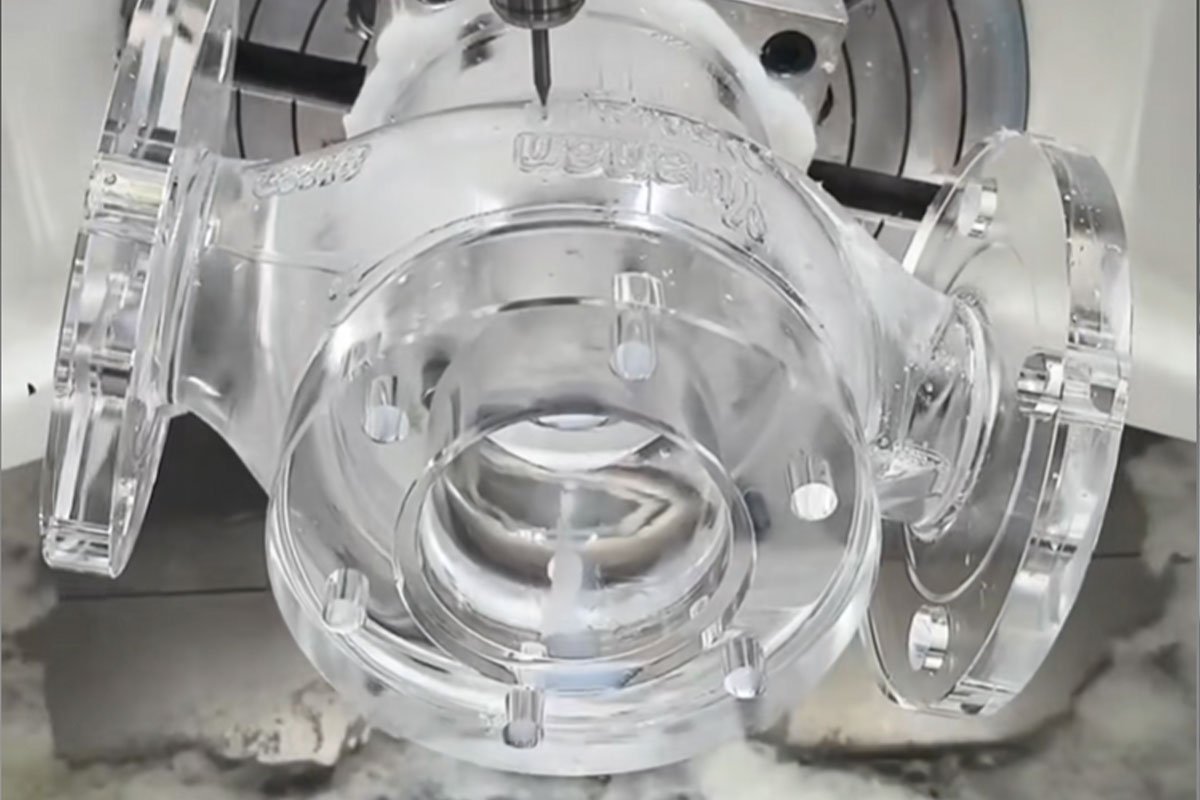
CNC milling is one of the most widely used methods in prototyping. It involves a rotating cutting tool that removes material from a stationary workpiece. This process is ideal for creating complex shapes, slots, pockets, and detailed surface features. With 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling machines, engineers can produce highly intricate prototypes with excellent precision and surface finish.
CNC Turning:
CNC turning is used for parts with cylindrical or symmetrical shapes, such as shafts, pins, or bushings. In this process, the workpiece rotates while a stationary cutting tool removes material. CNC lathes can achieve tight tolerances and smooth finishes, making turning a fast and cost-effective option for round components.
Most CNC prototype projects combine multiple operations—such as milling and drilling—within a single setup to improve accuracy and reduce production time. By selecting the right combination of CNC operations, manufacturers can produce high-quality prototypes that closely match final production parts in both form and function.
Share this article
Written by : Alex
A quick overview of the topics covered in this article.
Latest articles
March 3, 2026