Applications of CNC Machining in the Robotics & Automation Industry
CNC machining is the fundamental manufacturing process for producing high-precision structural and mechanical components within the robotics sector. From heavy-payload industrial arms to precise collaborative robots (cobots) and autonomous mobile platforms, CNC processes ensure the geometric tolerances required for accurate motion control and long-term reliability.
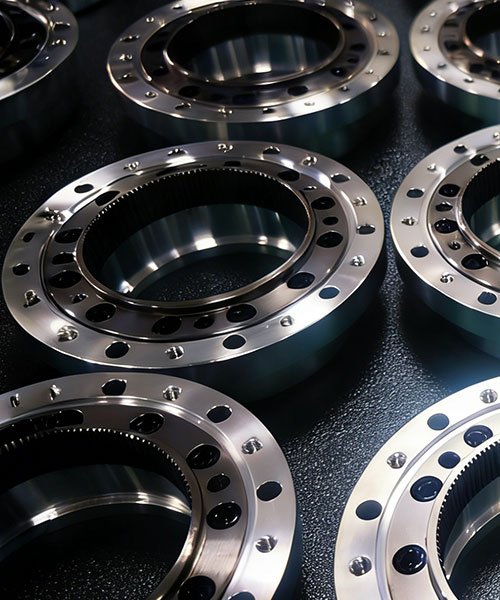

Joint and Drive System Components
The performance of a robotic arm relies heavily on the precision of its joints. CNC machining is utilized to fabricate critical drive components that require tight interference fits and concentricity.
- Gearbox Housings: Precision turning and milling of outer shells and spline hubs for Harmonic Drives and Cycloidal reducers. Tolerances are strictly controlled (typically within ±0.005mm) to ensure zero-backlash transmission.
- Motor Flanges: Machining of adapter plates that align servo motors with gearboxes, ensuring the transmission axis remains perfectly linear to prevent vibration.
- Drive Shafts: Turning of high-strength steel shafts used to transmit torque within the joint assembly.
Structural Links and Chassis
To maximize payload capacity and acceleration, robotic structures must balance rigidity with weight. CNC machining allows for “skeletonization”—removing material from non-load-bearing areas to reduce inertia.
- Robotic Arms (Links): Machining of upper and lower arm sections from solid blocks of Aluminum 6061 or 7075. The monolithic design eliminates the need for welding, providing superior structural integrity.
- Cross-Links and Castings: Post-machining of cast aluminum or iron bases to create precise mounting surfaces and bearing bores.
- AMR/AGV Chassis: Milling of base plates and frames for Autonomous Mobile Robots, ensuring flatness for the mounting of navigation sensors and payload lifters.
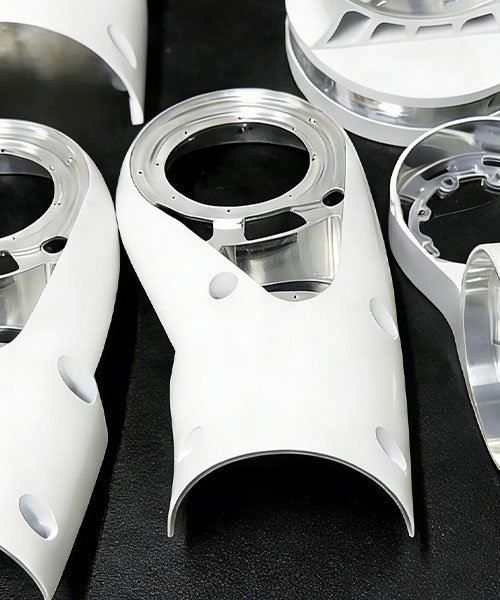
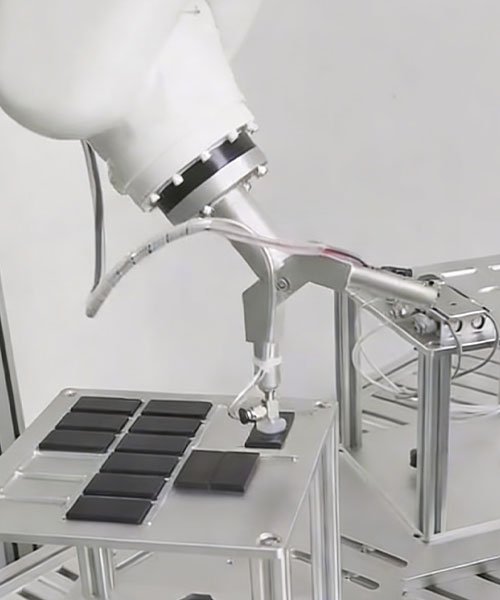


End-Effectors (EOAT) and Tooling
End-of-Arm Tooling requires high customization to suit specific production tasks. CNC machining offers the flexibility to produce custom grippers and fixtures without mold costs.
- Gripper Fingers: Custom machining of fingers from Aluminum or Steel to match the geometry of the workpiece being handled.
- Vacuum Plates: Drilling of complex internal air channels within suction plates to eliminate the need for external tubing.
- Adapter Plates: Interfaces that connect the robot wrist to various tools, requiring precise bolt patterns and dowel pin holes for repeatability.
Sensor Housings and Electronic Enclosures
Robotics systems rely on sensitive electronics for navigation and control. CNC machining provides robust protection and thermal management.
- LiDAR and Camera Mounts: Precision machining of brackets for vision systems. Dimensional stability is critical here to maintain calibration during robot movement.
- Heat Sinks: Milling of finned aluminum enclosures to dissipate heat generated by servo drivers and onboard computers.
- HMI Bezels: Machining of durable front panels for teach pendants and operator control units.
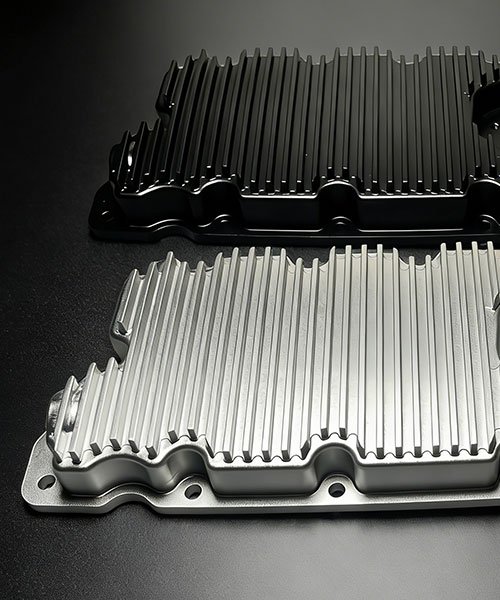
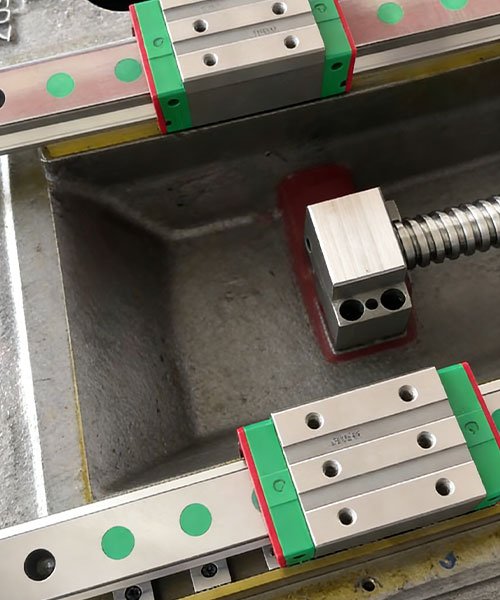


Assembly Fixtures and Jigs
Beyond the robot itself, CNC machining is essential for the automation environment surrounding the robot.
- Positioning Jigs: Manufacture of precision fixtures to hold workpieces in exact coordinates for robotic welding, assembly, or inspection.
- Conveyor Components: Turning of rollers, pulleys, and guide rails for automated material handling lines.
Advantages of CNC Machining for Robotics & Automation Industry
CNC machining offers distinct benefits for the manufacturing of automation hardware, addressing specific engineering challenges:
Precision and Motion Control
The process delivers tight tolerance robotic joints and gear housings. This precision is critical for minimizing backlash and ensuring accurate repeatability in industrial arms.
Material Performance
Machining enables the production of high-precision aluminum parts using grades like 7075-T6, as well as Magnesium alloys for ultra-lightweight requirements. The inclusion of Magnesium reduces inertia and absorbs mechanical vibration. This allows for structural components that maintain high rigidity, optimizing the robot’s payload-to-weight ratio.
Flexibility and Speed
CNC technology supports low-volume robotics manufacturing without the need for expensive molds. This facilitates the rapid development of custom end-effector machining solutions and prototypes, allowing for immediate design verification.
Machining Tolerances
We provide high-precision machining capable of holding tolerances down to ±0.005mm for critical features. This level of accuracy ensures that components strictly adhere to your dimensional specifications and assembly requirements.
| Category | Description |
| General Tolerances | Unless otherwise specified, standard tolerances for metals are ± 0.127 mm (± 0.005″) in accordance with ISO 2768-m. Tolerances for plastics and composites are generally ± 0.254 mm (± 0.010″) due to material properties. |
| Min Wall Thickness | Metals: 0.8 mm Plastics: 1.5 mm |
| Minimum Feature Size | 0.5 mm |
| Threads & Tapped Holes | M2 / #2-56 (Minimum) We can also machine custom threads. |
| Surface Finish | Unless post-processing is requested, parts are supplied with an as-machined surface of Ra 3.2 μm (125 μin). Visible tool marks may be present. |
| Edge Condition | Broken Edges (Deburred) |
| Maximum Part Size | CNC Milling: 4000×1500×600 mm; CNC Turning: 200×500 mm |
| Minimum Part Size | CNC Milling: 5×5×5 mm; CNC Turning: 2×2 mm |
Our Robotics & Automation Cases
This section presents our CNC machining projects for robotics and automation applications. These cases demonstrate our ability to produce high-precision components that support reliable operation in automated equipment, robotic assemblies, and industrial automation systems.
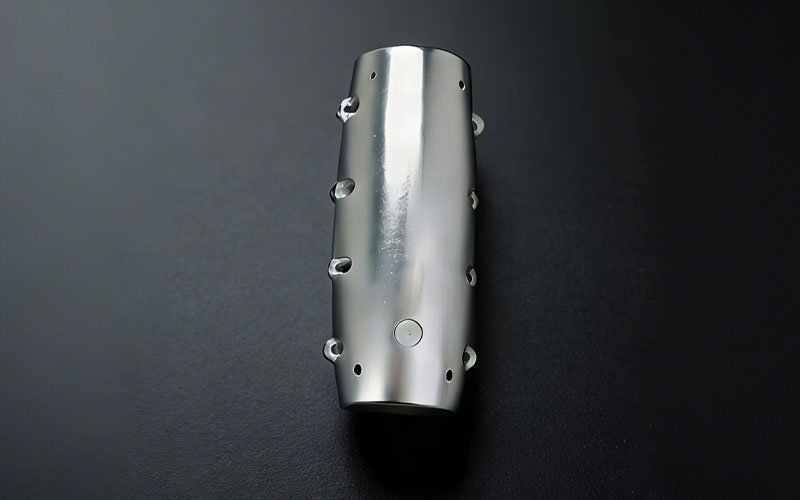
Magnesium CNC Machining Case: Lightweighting Robot Arm Shell
A European startup specializing in advanced robotics research approached [...]
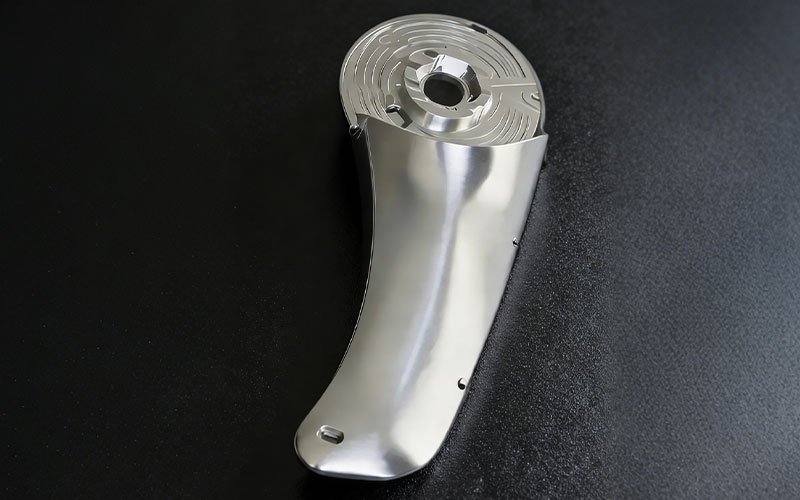
CNC Machined Aluminum 7075 Prototypes
Lightweighting for Robotics: CNC Machined Aluminum 7075 Prototypes for Humanoid [...]
FAQs About CNC Machining Services