Applications of CNC Machining in the Automotive Industry
CNC machining technology is integral to the automotive manufacturing supply chain, providing high-precision solutions for both internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and electric vehicles (EVs). From prototyping new concepts to manufacturing safety-critical suspension components, CNC processes ensure adherence to strict automotive standards.
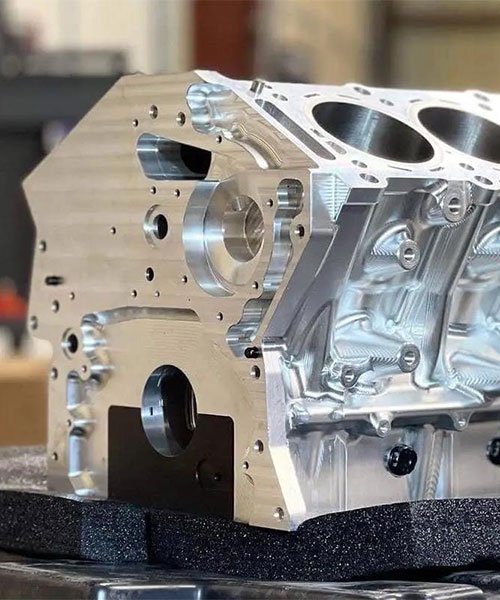

Engine and Powertrain Components
The powertrain requires components that can withstand high temperatures and rapid mechanical stress while maintaining micron-level tolerances for fluid and gas sealing.
- Cylinder Heads and Blocks: CNC milling is used to machine the mating surfaces and cylinder bores of engine blocks cast from aluminum or iron. This ensures a perfect seal for the head gasket and optimal piston movement.
- Transmission Housings: Complex gearboxes require precise bearing seats and oil channels. CNC machining ensures the concentricity of shafts and gears, reducing transmission noise and wear.
- Fluid System Components: Fuel rails, pumps, and valves are machined to manage high-pressure fluid dynamics efficiently.
Suspension and Chassis Parts
Suspension components are safety-critical parts that demand high structural integrity. CNC machining from solid billets (such as Aluminum 7075-T6) is often preferred over casting for high-performance applications to eliminate material porosity.
- Control Arms and Knuckles: Machining these parts allows for complex geometries that optimize the strength-to-weight ratio, contributing to overall vehicle lightweighting.
- Wheel Hubs and Brake Calipers: CNC turning and milling are used to manufacture hubs and multi-piston brake caliper housings, ensuring precise fitment and thermal stability under braking loads.
- Mounting Brackets: Custom brackets for securing engines or subframes are machined to handle specific vibration and load requirements.
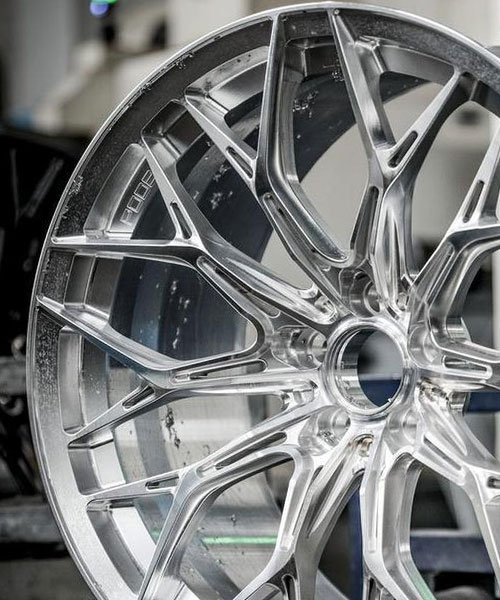
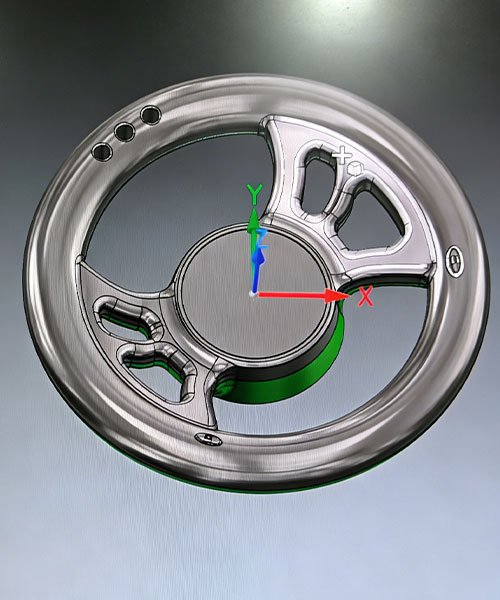


Interior and Cosmetic Components
For luxury and performance vehicles, the tactile feel and visual appearance of interior components are paramount. CNC machining creates metal parts with a premium finish that plastic molding cannot replicate.
- Dashboard Controls: Knobs, dials, and shifter paddles are machined to create a weighted, solid feel. Knurling textures are often applied for grip and aesthetics.
- Steering Wheel Components: Central hubs and spokes (as seen in billet steering wheels) are machined for custom designs, often finishing with bead blasting and anodizing.
- Trim Panels: Aluminum trim pieces are machined to fit complex dashboard contours with tight gaps.
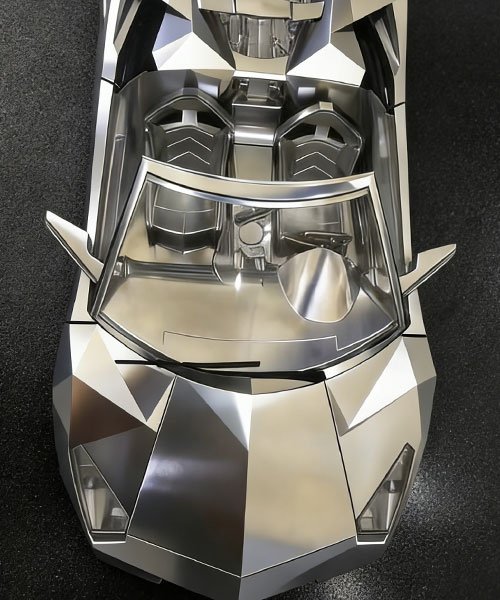
Rapid Prototyping and R&D
Before mass production tooling (such as molds or dies) is finalized, CNC machining is the standard method for validating designs.
- Functional Testing: Engineers use machined prototypes to test the fit, form, and function of a part in real-world conditions. For example, testing a machined aluminum manifold on a running engine dyno.
- Wind Tunnel Models: Scale models or full-size exterior components are machined for aerodynamic testing to verify drag coefficients.
- Fixture and Tooling Manufacturing: CNC machining is also used to create the jigs, fixtures, and molds that are subsequently used in the mass production assembly line.

Advantages of CNC Machining for Automotive Parts
CNC machining serves as a critical manufacturing process in the automotive lifecycle, offering distinct technical advantages over additive manufacturing (3D printing) and die-casting, particularly during R&D and low-volume production phases.
Rapid Iteration and Zero Tooling Costs
Unlike injection molding or die-casting, CNC machining requires no investment in expensive hard tooling (NRE costs). This allows engineering teams to modify designs and produce functional prototypes within days rather than weeks. This agility significantly accelerates the verification process for new vehicle programs and aftermarket modifications.
Superior Material Integrity
Automotive components machined from solid billet stock (e.g., Aluminum 7075, Stainless Steel) exhibit a homogeneous grain structure. This process eliminates internal porosity and voids often associated with cast parts. Consequently, machined parts offer higher tensile strength and fatigue resistance, making them suitable for safety-critical applications such as suspension control arms and brake calipers.
Strict Geometric Tolerances
Flight stability in aerodynamics and smooth operation in powertrains depend on precision. CNC machining delivers consistent accuracy with tolerances typically held within ±0.01mm. This level of precision is essential for engine components, piston heads, and bearing housings where strict adherence to Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) standards is required to ensure proper assembly fit.
Scalability for Low-Volume Production
For high-performance vehicles or limited-edition models, mass production methods are often economically unviable. CNC machining provides a scalable solution for production runs ranging from 50 to 1,000 units. It ensures that low-volume parts achieve the same quality and material properties as mass-produced components without the high setup costs.
Premium Surface Finishes
CNC machining produces parts without the layer lines visible in 3D printing or the rough texture of casting. This is critical for interior cosmetic parts (e.g., knobs, steering wheels) and exterior trim. Machined surfaces are readily prepared for secondary operations such as bead blasting, polishing, and anodizing to achieve automotive-grade aesthetics.
Machining Tolerances
We provide high-precision machining capable of holding tolerances down to ±0.005mm for critical features. This level of accuracy ensures that components strictly adhere to your dimensional specifications and assembly requirements.
| Category | Description |
| General Tolerances | Unless otherwise specified, standard tolerances for metals are ± 0.127 mm (± 0.005″) in accordance with ISO 2768-m. Tolerances for plastics and composites are generally ± 0.254 mm (± 0.010″) due to material properties. |
| Min Wall Thickness | Metals: 0.8 mm Plastics: 1.5 mm |
| Minimum Feature Size | 0.5 mm |
| Threads & Tapped Holes | M2 / #2-56 (Minimum) We can also machine custom threads. |
| Surface Finish | Unless post-processing is requested, parts are supplied with an as-machined surface of Ra 3.2 μm (125 μin). Visible tool marks may be present. |
| Edge Condition | Broken Edges (Deburred) |
| Maximum Part Size | CNC Milling: 4000×1500×600 mm; CNC Turning: 200×500 mm |
| Minimum Part Size | CNC Milling: 5×5×5 mm; CNC Turning: 2×2 mm |
Our Automotive Part CNC Machining Cases
This section showcases our CNC machining projects for automotive parts. We provide custom precision components for various automotive applications, with consistent quality and reliable performance to meet industry requirements.
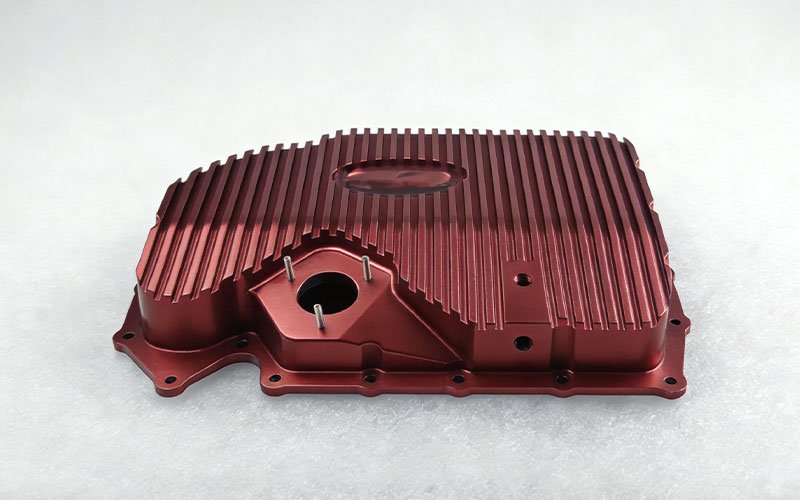
Custom CNC Machined Billet Aluminum Oil Pan for Performance Engines
A client contacted our facility to manufacture two units [...]
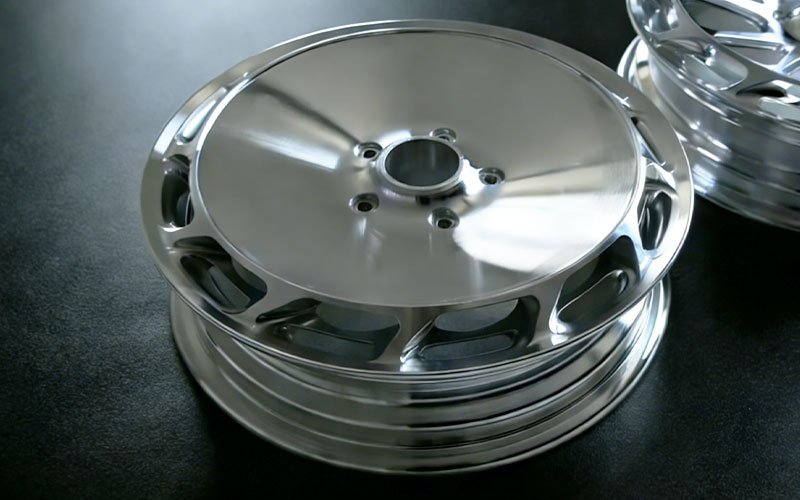
Custom CNC Machined Forged Aluminum Wheels
An automotive modification workshop contacted us, looking to customize [...]
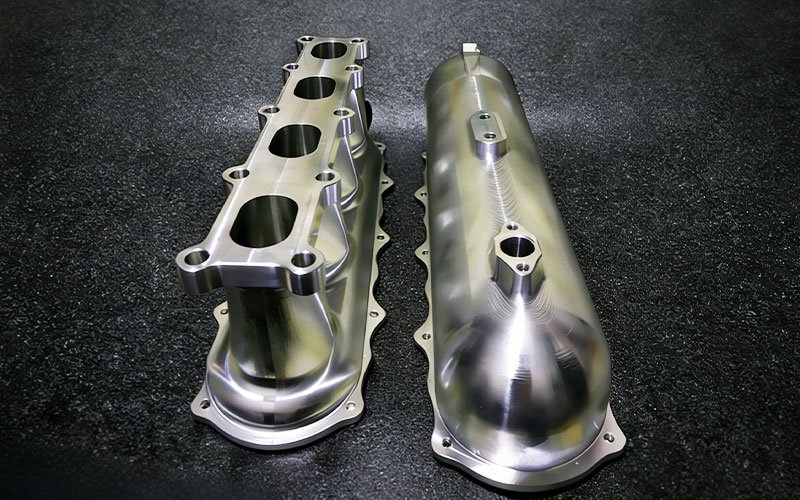
Custom Billet CNC Intake Manifold
An automotive modification workshop contacted us to manufacture a [...]
FAQs About CNC Machining Services